Microwave Drying
Heat-drying has become important in almost all areas of industrial processing. Apart from the popular conventional procedures based on conduction, convection, or infra-red radiation, heat-drying utilizing microwave energy is an attractive solution to many problems in process technology.
In terms of microwave drying the heat is generated by directly transforming the electromagnetic energy into kinetic molecular energy. The heat is generated deep within the fabric to be dried.
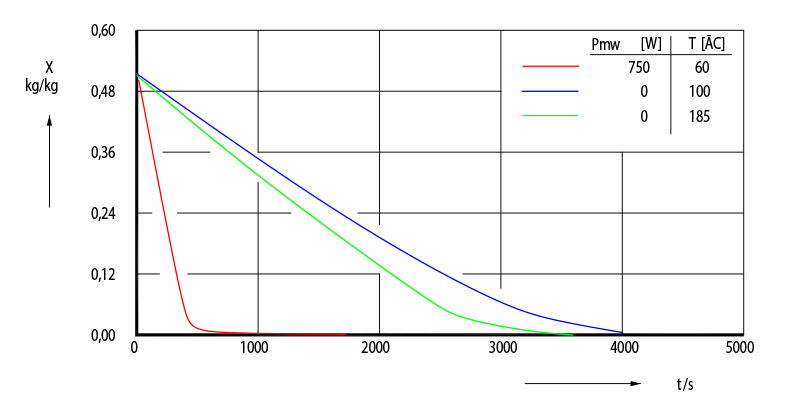
Drying material Al2O3 -granules, 2mm
X = moisture within the product, measured in kg/kg
Pmw = microwave power output as adjusted on the appliance
T = temperature [in °C] measured in the air-stream [ m3/h]
Advantages
As compared with conventional drying methods, which mean heating from the outside to the inside by heat conduction, microwaves show so-called volume heating and have following advantages:
- a temperature gradient directed towards the surface, i.e. temperatures inside are higher than outside, giving rise to a higher partial pressure that drives the evaporating liquid to the surface
- consequently, the superficial layer does not dry up completely and the surfaces remain permeable
- the liquid evaporating inside the product is emitted through the porous structure of the solid material’s macro-capillary system, resulting in a high drying velocity
- the heating of water and most organic solvents occurs selectively - due to the greater dielectric losses of water as compared to the product to be dried
- swift and thorough drying of moist products with low thermal conductivity
- static drying of thick layers without frictional losses
- high total efficiency of energy application
- high-speed control of the energy transport
- short processing times, i.e. suitable for automated manufacturing